Hydraulic energy is produced as long as
the prime mover which is usually an electric motor, drives the pump, and
hydraulic pressure develops resistance to pump flow. It causes damages to
the hydraulic pumps if the pump flow is not stopped or off-loaded i.e.
re-circulated back to tank when there is no action in the circuit. These
non-action periods arise from stalling an actuator, or by reaching the end
of the stroke or the circuit sequence, or during the time-delay periods of
the circuit sequence.
Hydraulic pump damages, power wastage and overheating of the hydraulic
fluid, circuit designers can be avoided by use of a variety of cleverly
designed systems that control maximum system pressure and pump flow during
non-action periods
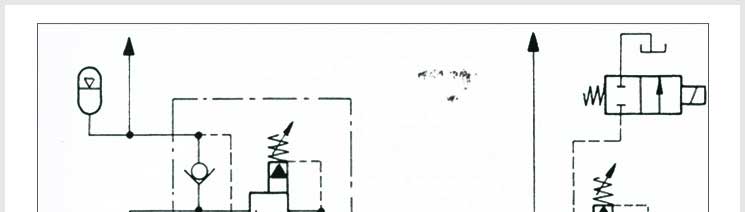
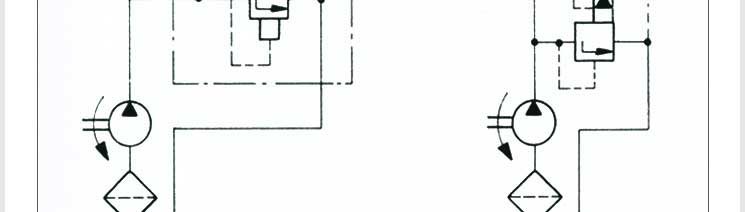
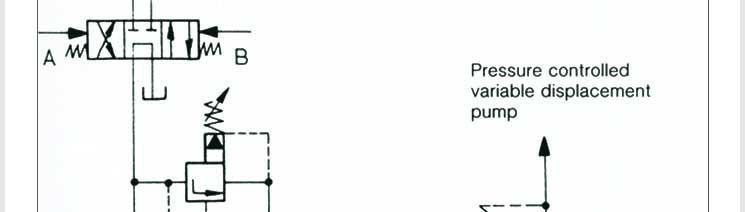
Pressure control valves control actuator force (force = pressure x area) and
determine (pre) select pressure levels at which certain machine operations
must occur and hence are used in hydraulic systems. The following are the
system functions of pressure control valve:
- To limit maximum system pressure in a hydraulic circuit or
sub-circuit, and thus provide overload protection.
- To provide re-direction of pump flow to tank, while system pressure
must be maintained (system un-loading).
- To provide re-direction of pump flow to tank while system pressure is
not maintained (system offloading).
- To offer resistance to fluid flow at selectable pressure levels
(counterbalance force).
- To provide an alternative flow path for the fluid at selected
pressure levels (pressure sequencing).
- To reduce (or step down) pressure levels from the main circuit to a
lower pressure in a sub-circuit.
These pressure control valves are often difficult to identify, owing to the
many descriptive names that have been applied to them. The function of the
valve in the circuit usually becomes the basis for its name. Following are
the names given to the valves for accomplish the above mentioned system
functions :
- Relief valves (direct-acting or compound)
- Unloading relief valve (accumulator charging valve)
- Offloading valve
- Counterbalance valve and Valve obrake valve
- Pressure-sequence valves (direct-acting or compound)
- Pressure-reducing valves (direct-acting or compound)